BCA Part J5.12 Heat rejection equipment
BCA Part J5.12 Heat rejection equipment
(a) The motor rated power of a fan in a cooling tower, closed circuit cooler or evaporative condenser must not exceed the allowances in Table J5.12.
(b) The fan in an air-cooled condenser must have a motor rated power of not more than 42 W for each kW of heat rejected from the refrigerant, when determined in accordance with AHRI 460 except for—
(i) a refrigerant chiller in an air-conditioning system that complies with the energy efficiency ratios in J5.10; or
(ii) packaged air-conditioners, split systems, and variable refrigerant flow air-conditioning equipment that complies with the energy efficiency ratios in J5.11.
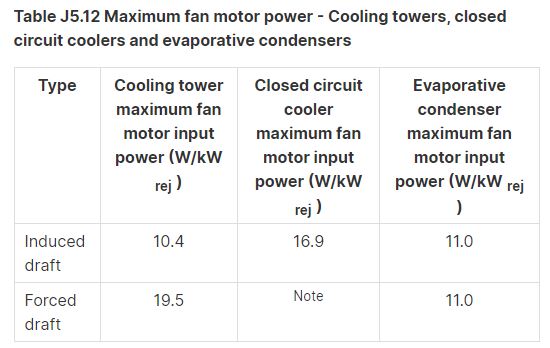
Table J5.12 Maximum fan motor power — Cooling towers, closed circuit coolers and evaporative condensers
[J5.12(a) outlines that the requirements for a fan, that is part of a cooling tower, closed circuit cooler or an evaporative cooler that is part of an air-conditioning system, are located in Table J5.12. The maximum fan motor power allowed is dependent on the type of fan used.
The performance of cooling tower fans, closed circuit cooler fans and evaporative condenser fans can be determined using any nationally or internationally accepted standard. For example Cooling Technology Institute’s (CTI) standard CTI STD-201RS(13) and Acceptance Testing Code (ATC) ATC-105(00), can be used to determine the performance of cooling tower fans. CTI STD-201RS(13) and ATC-105S(11) can be used for closed circuit cooler fans and ATC-106(11) can be used to determine the performance of evaporative condenser fans.
J5.12(b) states the requirements for a self-contained, air-cooled condenser fan motor that is part of an air-conditioning system. The fan motor must not consume more than 42 watts of fan motor power for each kW of heat removed from the refrigerant. The air-cooled condenser fan is used to cool refrigerant from its vapour phase to its liquid phase as part of the refrigeration cycle.
Air-cooled condensers, not part of a packaged air-conditioner or split unit as per the exemptions in J5.12(b)(i) and (ii), are typically associated with larger plant installations. The requirements of J5.12(b) are also not intended to capture a condenser covered by MEPS.]
Read more: BCA Part J5.5 Ductwork insulation
Read more: BCA Part J5.8 Pipework insulation
Read more: BCA Part J5.6 Ductwork sealing
Read more: BCA Part J5.9 Space heating
Read more: BCA Part J5.7 Pump systems
Read more: BCA Part J5.10 Refrigerant chillers
Read more: BCA Part J5.12 Heat rejection equipment
Related
Read more: Fan wall
Read more: How to verify the percentage of outside air in an enclosure
Read more: BCA Part J5 Air-conditioning system control
Read more: Microbial Induced Corrosion (MIC) in Pipes
Read more: Is your kitchen exhaust system a fire hazard
Read more: What is coanda effect